CAN-busskabelmontering är en fysisk anslutning som används i CAN-system (Controller Area Network). Dessa system är utformade för att underlätta kommunikationen mellan elektroniska enheter i olika applikationer, inklusive fordons- och industrisektorerna. Syftet är att överföra data mellan enheter i nätverket, så att de kan kommunicera med varandra på ett effektivt och tillförlitligt sätt.

När du väljer en CAN-busskabel ska du noga överväga datahastighet, kabellängd och driftsmiljö. Se tillverkarens specifikationer och rekommendationer för att välja rätt kabeltyp som uppfyller behoven i just ditt CAN-bussystem.
Det finns några huvudtyper av CAN-busskablar som beror på applikation, datahastighet och nätverkslängd.
Tvinnad parkabel- Detta är den vanligaste CAN-busskabeln. Den använder tvinnade ledarpar (ofta 2 par) för att minska störningar. För bättre EMI-störningar. Du kan välja STP-kabeln (Shielded Twisted Pair) som har en extra skärmande fläta eller folie runt de tvinnade paren. Vanliga kontakter är DEUTSCH DTM-kontakter, Molex MicroFit-kontakter och M-seriens cirkulära kontakter. 
Koaxialkabel, även kallad koaxialkabel, är en typ av kabel som ibland används i höghastighetstillämpningar med CAN-bussar (Controller Area Network). Den består av en enledarledare omgiven av en jordad skärmfläta, vilket bidrar till att minimera elektromagnetisk interferens (EMI) och signalförlust. Vanliga kontakter är BNC-kontakter eller cirkulära kontakter för flygplan.

Kabel med optisk fiber, även kallad fiberoptisk kabel, är en typ av kabel som är immun mot elektriska störningar och som vanligtvis används för att ansluta CAN-noder över längre avstånd. Fiberoptisk kabel består av tunna strängar av glas- eller plastfibrer som överför data med hjälp av ljusvågor. Detta gör den till ett idealiskt val för applikationer där höga hastigheter och långa avstånd krävs. Fibern ansluts med hjälp av optiska kontakter som CF8, ST eller anpassade terminaler.

Platt bandkabel-Ribbonkabel används ibland inom styrenheter och ECU:er. Kontakterna är vanligtvis anpassade flerpoliga kontakter eller IDC-kontakter.
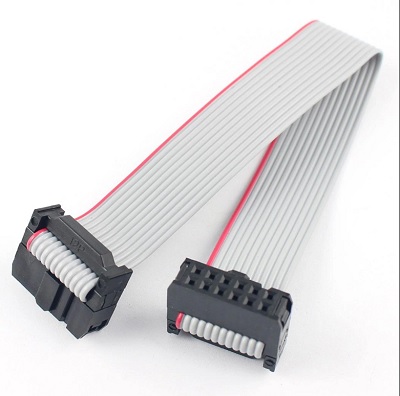
Här kan du läsa mer om de kontakter som vanligen används i ett CAN-bussystem:
DB9-anslutningar: Det här är 9-poliga kontakter som vanligtvis används för seriella anslutningar. De används ofta i enheter som CAN-bussanalysatorer eller gränssnitt för datorer.
OBD-II-anslutningar: Standard 16-polig kontakttyp, Dessa används vanligtvis i fordonsapplikationer. En OBD2-kontakt (On-Board Diagnostics II) gör det möjligt för en enhet att ansluta till diagnostiksystemet i en bil eller ett annat fordon.
Terminalblock: Dessa används ofta i industriella applikationer där det krävs en säker, trådbunden anslutning. De möjliggör en direktanslutning till CAN-bussen.
M12-kontakter: Det här är cirkulära kontakter som ofta används i industriella applikationer och applikationer i tuffa miljöer på grund av deras hållbarhet och motståndskraft mot damm och vatten.
D-Sub-kontakter: Det här är robusta och mångsidiga kontakter som finns i en mängd olika stiftantal, från 9 till 50. I CAN-bussystem är den 9-poliga versionen (DB9) vanligast.
Anslutningar för luftfart: Cirkulära kontakter avsedda för robust användning inom flygindustrin, t.ex. D38999/26-kontakter, används ibland för CAN i flyg- och rymdtillämpningar.
CAN-busskontakter används ofta i olika branscher, bland annat:
Industriell automation:CAN används i tuffa miljöer för kommunikation mellan enheter som sensorer, ställdon och styrenheter.
Fordon:Nästan alla moderna fordon har en CAN-buss som används för kommunikation mellan de många mikrokontroller som är inblandade i fordonets drift.
Luftfart:Vissa flygplan använder CAN för kommunikation mellan avionikutrustningar.
Hemautomation:CAN kan användas för kommunikation mellan smarta hem-enheter.
Marine:CAN-bussen används i vissa marina applikationer för kommunikation mellan olika system ombord.
Can-busskontakter ger en seriell kommunikationslänk med hög brusimmunitet, De stöder höghastighetskommunikation i realtid (upp till 1 Mbps) mellan elektroniska styrenheter (ECU) utan en värddator.
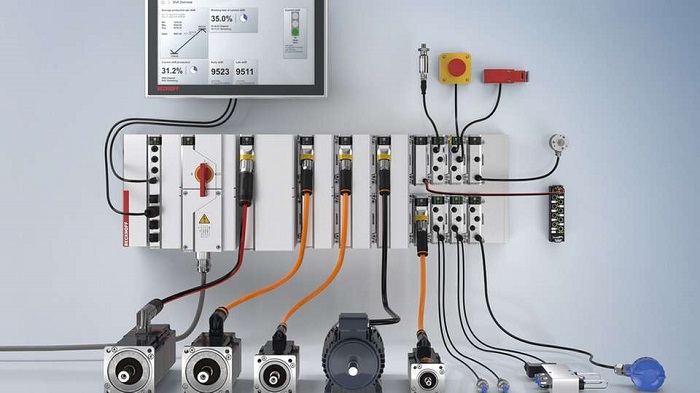
Hur CAN-bussystem fungerar i industriell kontrollapplikation:
I automationskontrollsystemet finns det flera robotarmar som måste arbeta tillsammans för att montera en produkt. Robotarmarna styrs av separata styrenheter. Robotarmarnas styrenheter måste kommunicera med varandra för att koordinera sina rörelser och dela sensordata. Detta sker med hjälp av ett CAN-bussnätverk.
Varje styrenhet för robotarmen har ett CAN-bussgränssnitt. Styrenheterna skickar meddelanden som innehåller information som aktuell position, hastighet, acceleration etc. över CAN-bussen till de andra styrenheterna. CAN-bussen ger snabb och tillförlitlig kommunikation mellan styrenheterna med minimal kabeldragning. Detta möjliggör ett sömlöst samarbete mellan robotarmarna för att optimera monteringsprocessen.
Förutom robotarmens styrenheter kan även sensorer, t.ex. kraftsensorer på robotens gripdon, anslutas till CAN-bussen. Sensordata kan överföras i realtid till styrenheterna. CAN-bussnätverket fungerar som en ryggrad som gör det möjligt för alla enheter att dela tidskritiska styrdata på ett smidigt och effektivt sätt. Detta ökar hastigheten och precisionen under tillverkningsprocessen samtidigt som det minskar komplexiteten i kabeldragningen.
Ytterligare enheter som HMI:er och dataloggare kan också läggas till i CAN-bussnätverket för att visualisera eller registrera data.
I exemplet är CAN-bussen det idealiska nätverket för att möjliggöra realtidskommunikation och styrning mellan flera enheter i industriella automationssystem. CAN-bussens brusimmunitet, hastighet och prioritetsbaserade meddelandehantering ger rätt egenskaper för sådana krävande applikationer.
CAN-bus är ett viktigt kommunikationsprotokoll som används i stor utsträckning inom industriell automation och kontrollapplikationer. Rätt val av CAN-bus-kontakter och -kablar är avgörande för att skapa ett robust, tillförlitligt och högpresterande nätverk. Faktorer som datahastighet, kabellängd och brusimmunitet måste beaktas när man väljer lämplig kabellösning. Vanliga kontaktdonstyper har alla sina egna fördelar beroende på användningsfallet, från skruvplintar för enkelhet till cirkulära kontakter av flygkvalitet för extrema miljöer. Sammantaget möjliggör CAN-bussen realtidsstyrning, interoperabilitet mellan enheter och minskad kabeldragning i industriella system. Genom att förstå vilka olika typer av CAN-busskontakter och -kablar som finns tillgängliga kan ingenjörer implementera robusta CAN-nätverk som fungerar tillförlitligt även i krävande industriella miljöer. Med den fortsatta utvecklingen av CAN-busstekniken kan vi förvänta oss att dess tillämpningar inom automation och styrning blir ännu mer mångsidiga och affärskritiska.
Om du vill ha mer information om Can bus-kabel/kontaktdon, vänligen kontakta info@flexcontac.com





